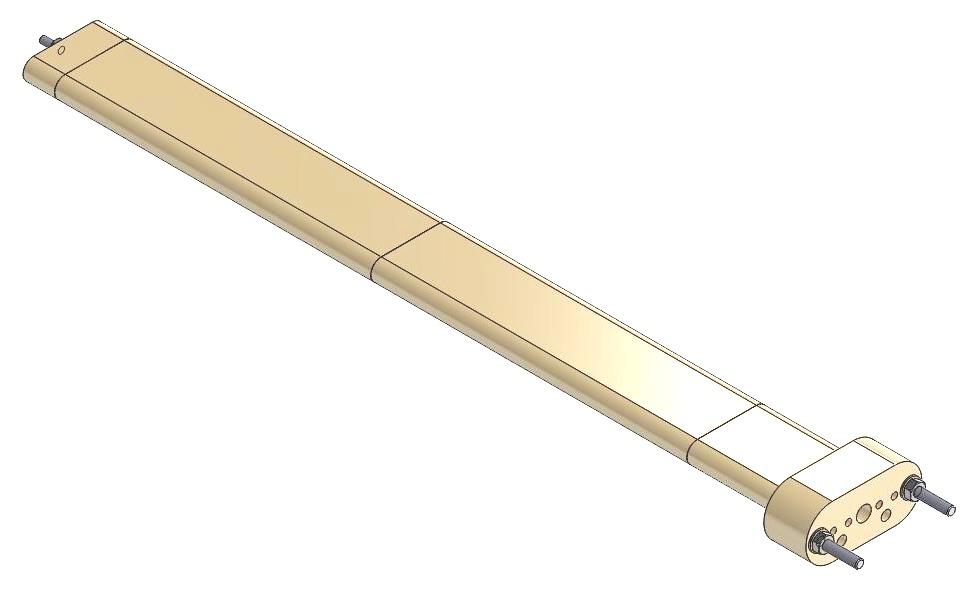
sectional ceramic heaters
Traditional solution for indirect heating
DESCRIPTION
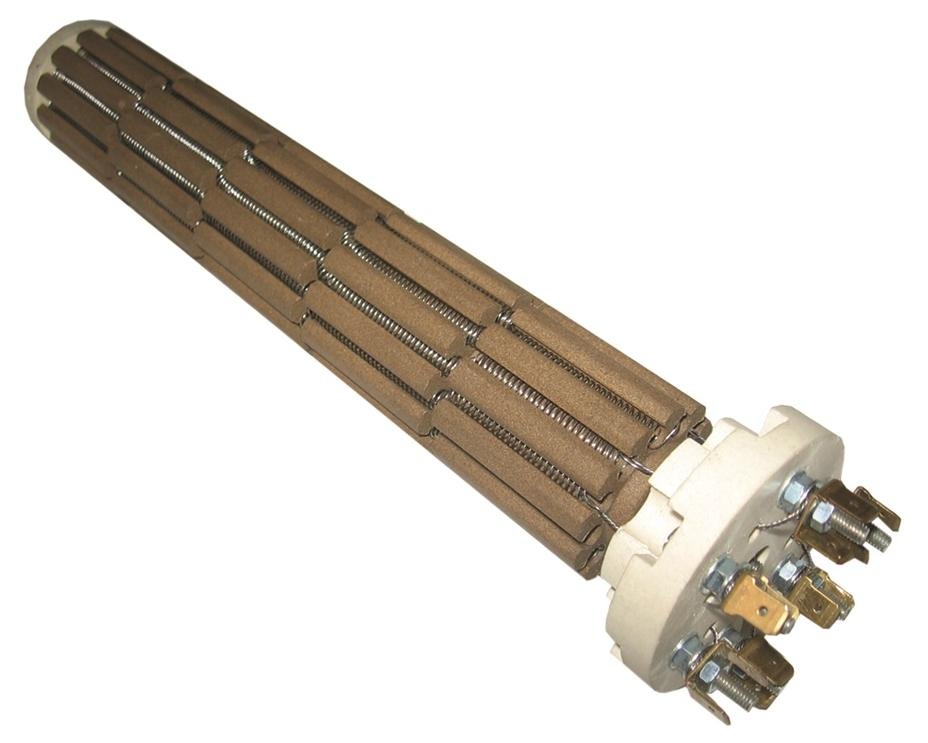
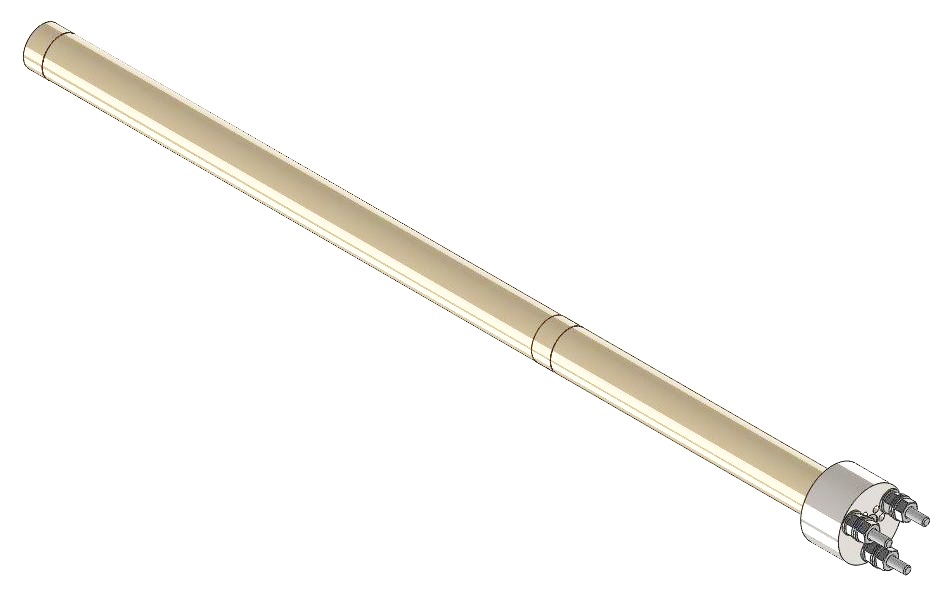
These heaters represent most usual solution for indirect heating of fluids and gases. Assembled into protective tube they are not in direct contact with fluid. Main advantage is possibility of simple and quick replacement of ceramic cartridge with resistance coil without dismantling protective tube. In addition, they are suitable for heating oil, bitumen and other mediums which can change the structure, carbonize and burn due to high temperatures on the heater surface which is common for system of direct heating.
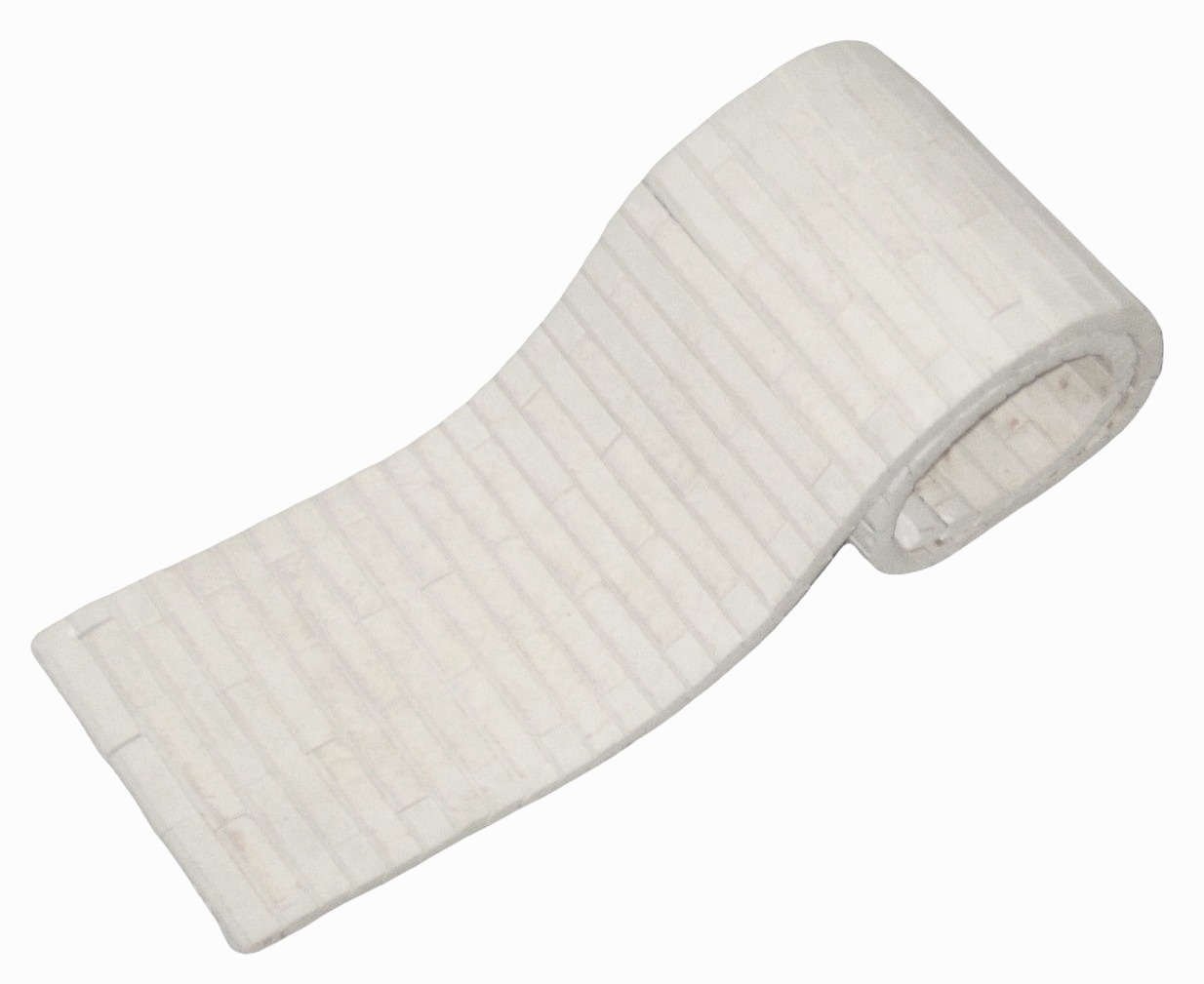
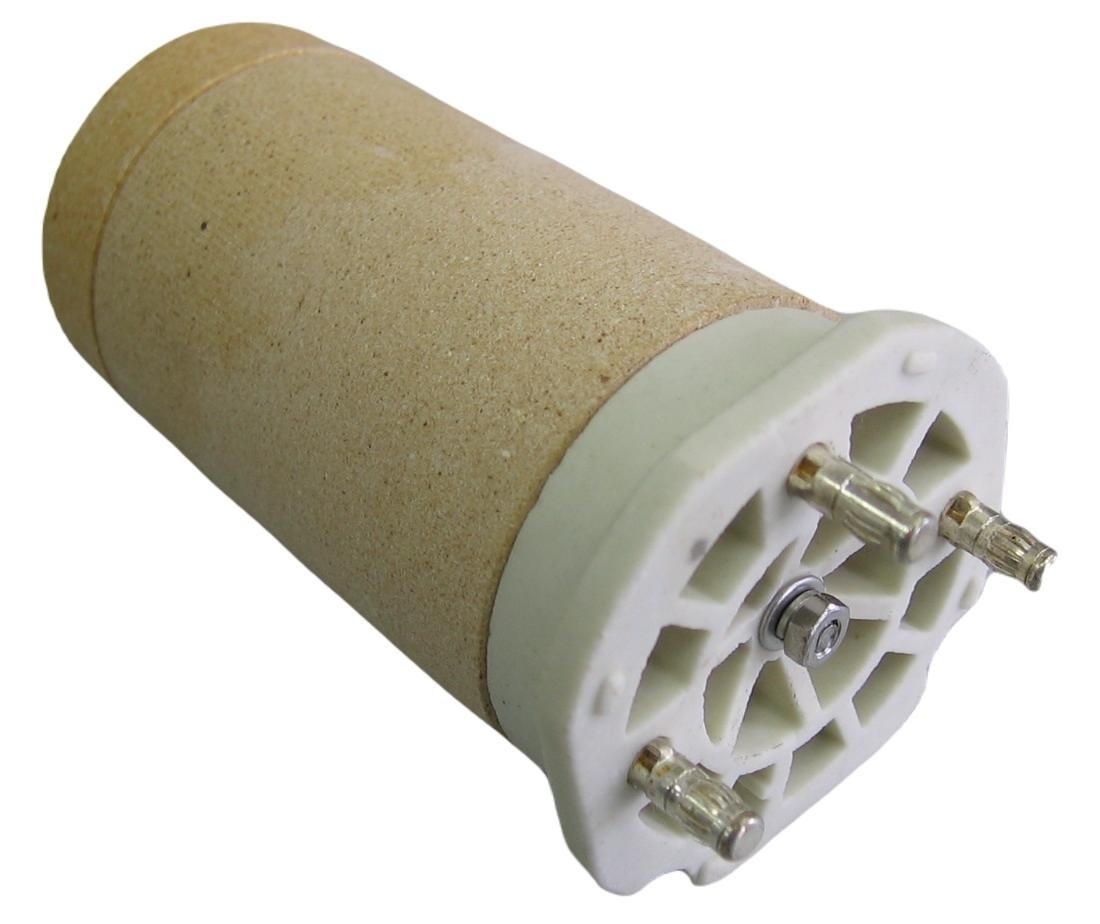
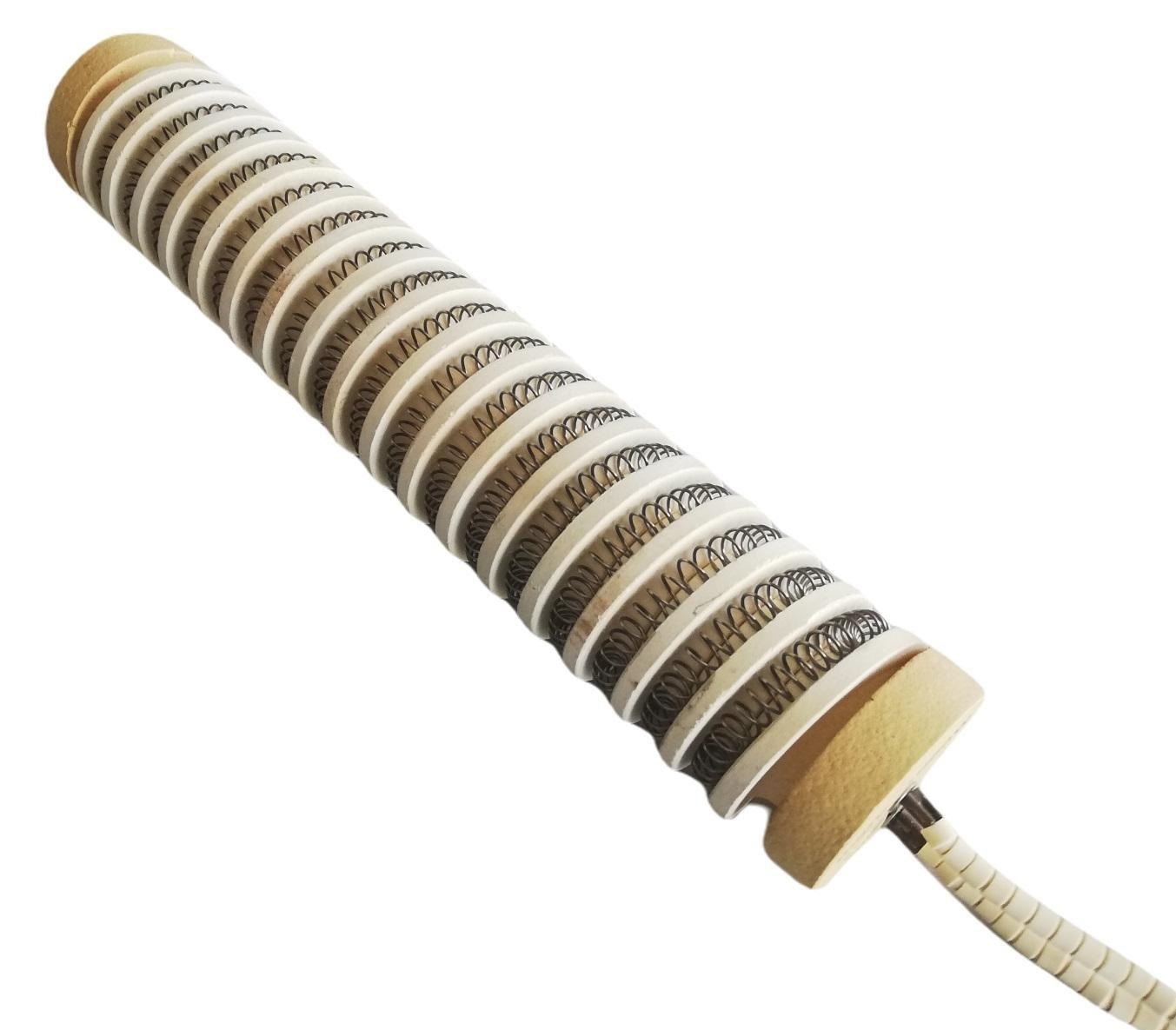
Ceramic sectional heaters have resistance coil embedded in grooves on ceramic stars - segments. Resistive wire (Ni-Cr) is used for coils whilst segments material is refractory technical ceramic.
APPLICATIONS
- Thermal oils, duplicators (reactors)
- Oils for lubrication, hydraulic oils, turbine oils, gearbox oils
- Drinking and technical water, both in open and closed systems
- Steam generators
- Fluids for cleaning, various solutions and emulsions
- Fuel oil, heavy oil, bitumen
- Fluids in galvanic baths, basins with diluted acids, alkaline baths
- Special fluids and gases, gases in steam form
- Dryers, industrial furnaces
Technical data
Type of heating | Indirect - liquid |
Material | Cordierite C520 |
Dimension | Heater diameter: Ø30, Ø32, Ø34, Ø36, Ø38, Ø41, Ø44, Ø46, Ø52, Ø54, Ø64mm Heater length: Max. 6000mm |
Assembly | Assembled into protective tube |
Connection | M4, M5, M6, tab terminals, cable |
Design | Standard range or acc. to customer specification Horizontal or vertical mounting position Open grooves on ceramic |
Other | Voltage: Single phase, two phase, three phase Surface load: for air 1 W/cm², for oil 2 W/cm², for water 4 W/cm² Optional: Protective tubes closed on one side, Flanges with threads or flat, Protective caps and housings |
Benefits
- Replacement of heater without emptying the container
- Dimensions, power and voltage upon request
- Heater is not in direct contact with fluid
- Suitable for heating of fluids which carbonize and burn due to high temperatures