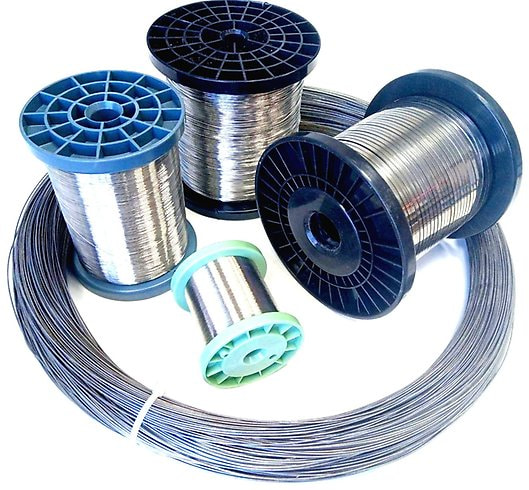
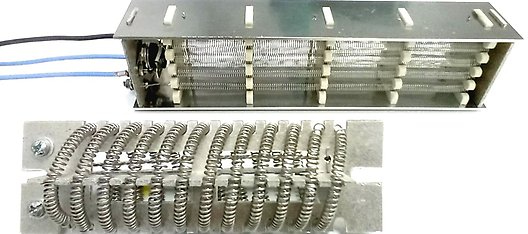
Resistance wires and ribbons
Austenitic and ferritic resistance heating alloys
DESCRIPTION
Resistance heating alloys are characterized by high and constant specific electrical resistance values. They are used wherever electrical energy is converted into heat. There are two main groups of alloys: The ferritic (FeCrAl) and the austenitic (NiCr) alloys.
NiCr 80/20 (up to 1200°C) is the austenitic alloy with the high nickel content. Because of its good properties, it is widely used in the electric appliance industry. FeCrAl 20/5 (up to 1300°C) is ferritic alloy that has higher resistivity and lower density, but also better heat resistance than austenitic alloys. Its features make it suitable for most applications in appliance industry, electronics and heating element production. FeCrAl 25/5 (up to 1400°C) is ferritic alloy commonly used in industrial furnaces and heat treatment processes. All alloys can be produced in different dimensions and shapes of cross sections, such as wires, rods, ribbons and strips.
APPLICATIONS
- Electric appliance industry
- Industrial furnaces and heat treatment plants
- Heating elements production
- Electronic components
- Brake and starting resistors
- Low temperature heating applications
Technical data
Type of heating | Radiation |
Material | Austenitic alloys: Ferritic alloys: |
Dimension | Wire diameter: from Ø0.06mm to Ø7.00mm Ribbon width: from 0.50mm to 30mm |
Assembly | Adapted for the application |
Connection | Adapted for the application |
Design | Round cross section: Wire, Rod |
Other | Maximum temperature: Up to 1200°C for NiCr 80/20 (2.4869) alloy Small sizes are available on spools (app. mass 3-6kg) |
Benefits
- Non-magnetic properties
- Better creep strength and hot strength
- Higher level of emissivity
- Better ductility after use
- Higher resistance to wet corrosion
Ferritic alloys benefits:
- Higher surface load and max. temperature
- Longer service life
- Better yield strength
- Higher electrical resistivity
- Better surface oxidation
- Lower density, weight savings
- Higher resistance to sulphur